Versickerung und Retention/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „Infiltration and Retention“) |
|||
| (195 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<languages /><br /> | <languages /><br /> | ||
| − | [[Datei:Rwv.jpg|border|200px|right|baseline| | + | [[Datei:Rwv.jpg|miniatur|border|200px|right|baseline|Infiltration and retention]] |
| − | In | + | In water management, experience asserts that rainwater should be infiltrated at the place where it accumulates. If this is not possible, then in many cases the temporary storage (attenuation or retention) of rainwater is required in attenuation volumes in order to protect the drainage systems from overloading and to limit their dimension. |
| − | + | Advantages of rainwater infiltration | |
| − | ''' | + | '''For end users:''' |
| − | * | + | *stormwater fees are saved |
| − | * | + | *the local microclimate is improved |
| − | ''' | + | '''For municipalities:''' |
| − | * | + | *lower costs for flood protection / flood prevention |
| − | * | + | *lower costs for sewer construction, sewer rehabilitation and sewage plant operation |
| − | * | + | *lower connection costs for new developments |
| − | * | + | *protection of the groundwater supply |
| − | ''' | + | '''Advantages of rainwater retention:''' |
| − | * | + | *limiting area discharge, reducing flood risk |
| − | * | + | *lower costs in sewer construction, sewer rehabilitation and sewage plant operation |
| − | * | + | *connection of new developments to existing, full-capacity drainage systems |
| − | * | + | *relief of overloaded sewer networks |
| − | = | + | =Basic principles= |
| − | == | + | ==Quality of rainwater runoff== |
| − | + | The runoff from paved surfaces are classified into the categories of non-hazardous, tolerable and intolerable according to their material concentration and thereby possibly associated potential hazards to groundwater in targeted rainwater infiltration. | |
| − | === | + | ===Non-hazardous rainwater runoff=== |
| − | + | Non-hazardous rainwater runoff can be infiltrated (e.g. in trenches) without pretreatment measures through the unsaturated zone (below the root zone and above the groundwater level). | |
| − | === | + | ===Tolerable rainwater runoff=== |
| − | + | Tolerable rainwater runoff can be infiltrated through the unsaturated zone after suitable pretreatment or using cleaning processes (sedimentation system, rainwater cisterns, overgrown soil, etc.). | |
| − | === | + | ===Intolerable rainwater runoff=== |
| − | + | Intolerable rainwater runoff can only be infiltrated after pretreatment. | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Surface / Area !! Qualitative evaluation |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Green roofs, fields and cultivated land; roof surfaces without the use of uncoated metals (copper, zinc and lead), terrace surfaces in residential and similar commercial areas || non-hazardous |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Roofs with usual proportions of uncoated metals, cycle tracks and footpaths in residential areas, calm traffic areas; lawns and car parking without frequent vehicle changes; as well as lightly used vehicle areas (up to DTV 300 vehicles); streets with DTV 300 - 5,000 vehicles, e.g. access roads, residential and district streets; airport tarmac; roofs in commercial and industrial areas with significant air pollution, see DWA-A138. || tolerable |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Lawns and streets in commercial and industrial areas with significant air pollution; for special zones see DWA || intolerable |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Source DWA-A138, DTV = average daily traffic intensity | |
| − | == | + | ==Soil composition== |
| − | === | + | ===Infiltration capacity of the soil=== |
| − | [[Datei: | + | [[Datei:RWV_Versickerungsfähigkeit_en.png| miniatur|300px|Overview of different kf-values for soils]] |
| − | + | The underground composition is of crucial importance for rainwater infiltration. The permeability coefficient (kf-value) is a measure of water permeability of the soil. The permeability coefficient should be between 10<sup>-3</sup> and 10<sup>-6</sup> in order to ensure the functionality of the infiltration system. | |
| − | + | In order to avoid over-dimensioning of the system, the kf-value should be determined as accurately as possible through investigation. There are professional geotechnical experts for this purpose. | |
| − | === | + | ===Quick test for soil composition=== |
| − | + | If the kf-value is unknown, then an approximation of the underground infiltration can be isolated based on the following short test. | |
| − | [[Datei: | + | [[Datei:RWV_Testgrube_en.png|miniatur|300px |Test pit]] |
| − | # | + | #Dig a 50 x 50 cm wide and approx. 30 cm deep pit. Important: Do not enter the pit to avoid compression! |
| − | # | + | #Cover the soil with a gravel layer to prevent soil flotation. Insert a measuring rod into the ground. 10 cm above the pit bottom place a mark on the measuring rod. |
| − | # | + | #Now fill the pit with water and replenish for 1-2 hours regularly (e.g. garden hose). |
| − | # | + | #Fill water up to the mark. After 10 minutes, fill as much water as necessary to raise the water level back to the mark using a measuring bucket. The soil permeability can be estimated from the quantity of refilled water. |
| − | # | + | #Repeat step 4 as many times (at least 3 times), until a consistent value is established. |
| − | + | Evaluation: | |
| − | + | Water quantity < 1.5 litres in 10 minutes: little infiltration possible (silt)<br /> | |
| − | + | Water quantity = 1.5 litres in 10 minutes: infiltration possible (silty sand)<br /> | |
| − | + | Water quantity > 3 litres in 10 minutes: good infiltration possible (sand, gravel)<br /> | |
| − | == | + | ==Cleaning options for precipitation water== |
| − | + | The contamination of underground and surface water from rainwater from roofs and traffic areas can be considered qualitatively and quantitatively by using simple assessment procedures (ATV DVWK-M153). Depending on the result, various measures for handling rainwater must be taken to ensure adequate water protection. | |
| − | + | For discharge into a trench, minimum protection requires coarse filtration. | |
| − | :''' | + | :'''Important: with rainwater harvesting cisterns'''<br /> |
| − | + | According to DIN 1989-1, underground infiltrations systems (trenches) are equivalent to infiltration systems in active soil areas in terms of qualitative aspects, provided the inlet water comes from a rainwater harvesting system with non-metallic roof areas. | |
| − | === | + | ===Sedimentation and filter chamber, sedimentation systems=== |
| − | [[Datei:RWV_Filterschacht.png |miniatur|300px|Sedimentation | + | [[Datei:RWV_Filterschacht.png |miniatur|300px|Sedimentation and filter chamber]] |
| − | + | Systems with a settling chamber in which the flow conditions allow specific substances heavier than water sink and specific lighter substances float are referred to as sedimentation systems. | |
| − | + | Collection and filter chambers consist of a sedimentation area in which heavy particles settle and a filter that prevents light coarse contaminants from entering the downstream storage. Even light materials are retained in the chamber with an immersion pipe. Depending on the amount of dirt, they must be cleaned regularly. The total water discharged from roof is filtered and supplied to the tank. In Germany the chambers are designed in accordance with ATV DVWK-M153, corresponding to the expected amount of dirt and connected roof area. | |
| − | === | + | ===Soil passages=== |
| − | [[Datei:RWV Bodenpassagen.png|miniatur|300px| | + | [[Datei:RWV Bodenpassagen.png|miniatur|300px|Soil passages]] |
| − | + | Contaminants from flowing rainwater are retained and stored or degraded by physical, chemical and if necessary, biological processes with passage through soil layers or in trough-trench systems or unsealed surfaces such as grass pavers. Thus passage through overgrown topsoil is more effective than through a non-vegetated soil zone. The protective cover layers over groundwater must not be penetrated. | |
| − | === | + | ===Flushable and camera-accessible trenches=== |
| − | + | Should contaminants penetrate into the trench despite pre-cleaning, it is very important that subsequent cleaning is possible. In many trenches e.g. box systems, only the flushing ducts can be cleaned afterwards. However fine contaminates pass through the slots in the flushing ducts and gradually clog the floors and walls of these trenches. Ultimately these can only be dug out completely if they have lost their infiltration capacity. With [https://www.intewa.de/en/products/drainmax/ DRAINMAX] Tunnel trenches for example, the critical walls and floors can be inspected with a camera through adequate connection chambers and are completely flushable. Contaminants either are retained in the coarse filter of the sedimentation and filter chamber or settle in the sedimentation area. The coarse filter can be removed and emptied after the flushing process. The parallel rows of trenches are additionally protected by the long settling section in the seepage pipe and the additional settling possibility in the inspection and flushing chamber. This guarantees a constant infiltration performance long-term. | |
| − | = | + | =Construction of an infiltration system= |
| − | + | #Distance to MHGW (mean highest groundwater level) from the bottom of the system: > 1 m | |
| − | + | #Soil permeability > 1 x 10<sup>-6</sup> (with lower values see retention) | |
| − | + | #Soil permeability < 1 x 10<sup>-3</sup> (with higher permeability too little treatment) | |
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''Trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel''' |
| + | |||
| + | [[Datei:RWV_Rigolenversickerung_DM.png|600px|Trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel]] | ||
| + | <table style="width:600px"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 5. Topsoil</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">2. Tunnel side and top backfill</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">6. Sedimentation/filter chamber</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">3. Geotextile</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">7. Rainwater inlet</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">4. Tunnel overburden</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Trough-trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Datei:RWV_Mulden_Rigolenversickerung_DM.png |600px | Trough-trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel]] | ||
| + | <table style="width:600px"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 6. Infiltration trough</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">2. Tunnel side and top backfil</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">7. Rainwater inlet</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">3. Geotextile</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">8. Distance to groundwater</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">4. Tunnel overburden</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">9. Active soil zone</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">5. Topsoil</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">10. Maximum water level</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''DRAINMAX Tunnel System | + | '''DRAINMAX Tunnel System for commercial properties''' |
| − | [[Datei:RWV_System_Gewerbeobjekte_DM.png |600px | DRAINMAX Tunnel System | + | [[Datei:RWV_System_Gewerbeobjekte_DM.png |600px| DRAINMAX Tunnel System for commercial properties]] |
| − | + | <table style="width:600px"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 7. Sedimentation/filter chamber</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">2. Tunnel side and top backfill</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">8. Flushing chamber</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">3. Geotextile</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">9. Rainwater inlet</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">4. Tunnel overburden</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">10. Maximum water level</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">5. Topsoil</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">11. Geotextile composite bottom layer</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top">6. Rainwater distribution</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| − | = | + | =Construction of a retention system= |
| − | == | + | ==Retention volume== |
| − | [[Datei:RWV Drosselablauf.jpg |miniatur|200px| | + | [[Datei:RWV Drosselablauf.jpg |miniatur|200px|Retention cistern with throttle discharge]] |
| − | [[Datei:RWN DrosselablaufNutzvolumen.png.jpg|miniatur|200px| | + | [[Datei:RWN DrosselablaufNutzvolumen.png.jpg|miniatur|200px|Retention cistern with throttle discharge and usable volume]] |
| − | + | There are several options for the retention of rainwater: | |
| − | * | + | *Storage with pure retention and throttle discharge |
| − | * | + | *Storage with combined retention and use and throttle discharge |
| − | + | The combination of rainwater harvesting and rainwater retention in a cistern is particularly interesting for smaller systems for single-family homes since the costs for excavation and delivery are incurred only once and the cistern is not significantly more expensive. | |
| − | * Retention | + | * Retention with approved partial infiltration and throttle discharge |
| − | + | With permitted partial infiltration, the [https://www.intewa.de/en/products/drainmax/ DRAINMAX] system with tunnel elements is an extremely interesting alternative. The low height offset between inlet and outlet in combination with large space flexibility and a very high storage volume are the advantages of this variant. If no water is allowed to enter the surrounding soil from the system, it can be sealed with an EPDM foil on site. | |
| − | [[Datei:RWV_DM_System.png|600px|DRAINMAX Tunnel | + | [[Datei:RWV_DM_System.png|600px|DRAINMAX Tunnel system]] |
| − | + | <table style="width:600px"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 6. Topsoil</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 2. Tunnel side and top backfill</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 7. Sedimentation/filter chamber</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 3. Geotextile</td> | |
| − | + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 8. Throttle chamber</td> | |
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 4. Enclosed sheet basin made from EPDM and geotextile</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 9. Discharge throttle</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 5. Tunnel overburden</td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:50%; text-align: left; vertical-align: top"> 10. Rainwater inlet</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Throttle discharge== |
| − | + | In a retention system the water is supplied into the drainage system with a throttled flow rate. The throttle discharge corresponds to the permitted outflow of the sealed area connected to the drainage system. Most of the time this discharge corresponds to the natural flow before sealing the area. | |
| − | + | In the retention system the permissible throttle discharge is either supplied to a downstream drainage system by means of a lift pump or through a discharge throttle provided the height conditions allow. According to DWA-A 117, the arithmetic average of the values of the throttle curve is to be set for uncontrolled throttling (fixed throttle/vortex throttle). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Compared to the vortex or fixed throttle, continuous throttles make sure that the maximum permitted water quantity Q drains constantly, irrespective of the impounding depth H. As a result, the retention tank with continuous throttle can be dimensioned by 10% to 30% smaller than with fixed throttle discharge or vortex throttles. | |
| − | [[Datei:starreDrossel.png|miniatur|200px| | + | [[Datei:starreDrossel.png|miniatur|200px|Fixed throttle]] |
| − | [[Datei:Wirbeldrossel.png|miniatur|200px| | + | [[Datei:Wirbeldrossel.png|miniatur|200px|Vortex throttle]] |
| − | [[Datei:KontinuierlicheDrossel.png|miniatur|200px| | + | [[Datei:KontinuierlicheDrossel.png|miniatur|200px|Continuous throttle]] |
| − | + | Exp. throttle curve for maximum admissible water quantity of 31 L/s | |
| − | [[Datei:Drosseldiagramm.png |300px| | + | [[Datei:Drosseldiagramm.png|300px|Throttle diagram]] |
| − | 1. | + | 1. Fixed throttle (arithmetic mean = 21 L/s) |
| − | 2. | + | 2. Vortex throttle (arithmetic mean = 21 L/s) |
| − | 3. | + | 3. Continuous discharge throttle (31 L/s) |
| − | === | + | ===Fixed throttle=== |
| − | + | The simplest form of a fixed or static throttle is a simple flow restrictor. The discharge value Q of the fixed throttle depends on the hydrostatic pressure resulting from the impounding depth H. | |
| − | === | + | ===Vortex throttle=== |
| − | + | A spiral stream of variable strength with a central rotating air core is formed by the tangential feed in the vortex throttle depending on the water level. However this does not lead to a continuous throttle outflow. The vortex throttle has the advantage of requiring less space and lower risk of blockages due to the larger remaining cross-section compared to the other throttle types. These advantages are rarely relevant with decentralized rainwater retention. | |
| − | === | + | ===Continuous throttle=== |
| − | + | The outlet flow is constant with the continuous discharge throttle irrespective of the impounding depth H. The float adjusts the restrictor opening at the impounding depth by means of a lever arm. Coarse pre-cleaning of rainwater is necessary for the trouble-free operation of the throttle. | |
| − | === | + | ===Calculation example of required storage volume=== |
| − | + | The crucial rain yield r<sub>D(n)</sub>, the duration D and frequency n [L/s-ha] must be determined iteratively (see Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems). | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|colspan="2" style="text-align:center" | '''V<sub>erf</sub> = ((A<sub>red</sub> x r<sub>D(n)</sub> x 10<sup>-4</sup>) – Q<sub>dr</sub> ) x D x 60 x 10<sup>-3</sup>''' | |colspan="2" style="text-align:center" | '''V<sub>erf</sub> = ((A<sub>red</sub> x r<sub>D(n)</sub> x 10<sup>-4</sup>) – Q<sub>dr</sub> ) x D x 60 x 10<sup>-3</sup>''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | V<sub>erf</sub> || = | + | | V<sub>erf</sub> || = required storage volume in m³ |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | A<sub>red</sub> || = | + | | A<sub>red</sub> || = connected paved surfaces in m² (5,000 m² in example) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = | + | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = crucial rainfall in L/sha (e.g. KOSTRA-Data Aachen, see Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Q<sub>dr</sub> || = | + | | Q<sub>dr</sub> || = discharge throttle value in L/s (the arithmetic mean of the throttle curve with non-continuous throttles, see diagram of throttle curves, 21 L/s in the example) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | D || = | + | | D || = Duration in min (in example, 30 min with the fixed throttle and vortex throttle, 20 min with the continuous throttle) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="text-align:left" | ''' | + | |colspan="2" style="text-align:left" | '''fixed throttle = vortex throttle:''' V<sub>erf</sub> = ((5,000 x 104.8 x 10<sup>-4</sup>) – 21) x 30 x 60 x 10<sup>-3</sup> = 56.6 m³ |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="text-align:left" | ''' | + | |colspan="2" style="text-align:left" | '''continuous throttle:''' V<sub>erf</sub> = ((5,000 x 131.7 x 10<sup>-4</sup>) – 31) x 20 x 60 x 10-3 = 41.8 m³ (- 26 %) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The larger the permitted throttle outflow in relation to the connected areas, the greater the difference. This difference leads to correspondingly lower total costs for the retention system. | |
| − | = | + | =Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems= |
| − | + | Also see [https://www.intewa.de/en/online-planner/ Online Planner] | |
| − | == | + | ==Rainwater runoff== |
| − | + | The calculation of rainwater runoff is based on the knowledge that heavy rains last short durations and low rains persist for longer. The rainfall yield declines at the same statistical frequency with increasing rainfall duration. The relationship between rainfall yield, duration and frequency is determined by the statistical analysis of precipitation registrations. Simple calculation methods in Germany are used in accord with DWA-A 117. For this a statistical rainfall with selected duration '''D''' and frequency '''n''' should be used as load case for calculation. For the determination of rain yield refer to the "amount of heavy peak rainfall in Germany - KOSTRA" (see table for a sample location). | |
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Rain duration D !! r <sub>D(1)</sub> l/(sha) !! r <sub>D(0,2)</sub> l/(sha) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 5 min || 135 | + | | 5 min || 135.0 || 243.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 10 min || 113 | + | | 10 min || 113.0 || 183.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 15 min || 97 | + | | 15 min || 97.2 || 152.6 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 20 min || 85 | + | | 20 min || 85.3 || 131.7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 30 min || 69 | + | | 30 min || 69.5 ||104.8 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 45 min || 52 | + | | 45 min || 52.9 || 81.2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 60 min || 43 | + | | 60 min || 43.1 || 66.8 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 90 min || 32 | + | | 90 min || 32.3 || 49.7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2 h || 26 | + | | 2 h || 26.4 || 40.3 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 3 h || 19 | + | | 3 h || 19.8 || 29.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 4 h || 16 | + | | 4 h || 16.1 || 24.3 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 6 h || 12 | + | | 6 h || 12.1 || 18.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 9 h || 9 | + | | 9 h || 9.1 || 13.4 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 12 h || 7 | + | | 12 h || 7.4 || 10.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 18 h || 5 | + | | 18 h || 5.4 || 7.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 24 h || 4 | + | | 24 h || 4.3 || 6.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 48 h || 2 | + | | 48 h || 2.6 || 3.7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 72 h || 2 | + | | 72 h || 2.1 || 2.9 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | ''KOSTRA | + | ''KOSTRA data sample location'' |
| − | === | + | ===Inflow to infiltration or retention systems=== |
:'''Q<sub>zu</sub> = 10<sup>-7</sup> x r<sub>D(n)</sub> x A<sub>red</sub> (1.)''' | :'''Q<sub>zu</sub> = 10<sup>-7</sup> x r<sub>D(n)</sub> x A<sub>red</sub> (1.)''' | ||
| Zeile 292: | Zeile 332: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Q<sub>zu</sub> || = | + | | Q<sub>zu</sub> || = Inflow to infiltration system in m³/s |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = | + | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = Rain yield for duration D and frequency n [L/sha] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | A<sub>red</sub> || = | + | | A<sub>red</sub> || = connected paved areas in m² |
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Discharge from the infiltration system=== |
| − | + | Darcy’s Law is used to calculate the discharge from an infiltration system: | |
| − | |||
:'''Q<sub>s</sub> = (b+0,5h) x L x ½ x k<sub>f</sub> (2.a)''' | :'''Q<sub>s</sub> = (b+0,5h) x L x ½ x k<sub>f</sub> (2.a)''' | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | k<sub>f</sub> || = | + | | k<sub>f</sub> || = Permeability coefficient of the saturated soil in m/s |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | b || = | + | | b || = Bottom width of the trench in m |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | h || = | + | | h || = Height of the trench in m |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | L || = | + | | L || = Length of the trench in m |
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Discharge from the retention system=== |
| − | + | ===Continuity condition=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | ||
:'''V<sub>erf</sub> = L x b x h x s<sub>RR</sub> = (∑Q<sub>zu</sub> - ∑Q<sub>s</sub>) x D x 60 (3.)''' | :'''V<sub>erf</sub> = L x b x h x s<sub>RR</sub> = (∑Q<sub>zu</sub> - ∑Q<sub>s</sub>) x D x 60 (3.)''' | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | V<sub>erf</sub> || = | + | | V<sub>erf</sub> || = required storage volume in m³ |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | D || = | + | | D || = Rain duration in min |
|} | |} | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Infiltration:'' |
| − | + | If only formulas 1. and 2.a are used for formula 3 to calculate L, then this will result in a significant trench length and volume. | |
| + | |||
| + | <math> = \dfrac {A_u \cdot 10^{-7} \cdot r_{D(n)}} {\tfrac {b_R \cdot h_R \cdot s_{RR}}{D \cdot 60 \cdot f_Z} + (b_R + \frac {h_R}{2}) \cdot \frac {k_f}{2}} </math> | ||
| − | + | S<sub>RR</sub> = Storage coefficient of the trench | |
| − | + | ''Retention'': | |
| + | Here, only formulas 1. and 2.b are used in formula 3. V<sub>er</sub> = (∑Q<sub>zu</sub> - ∑Q<sub>s</sub>) x D x 60''' | ||
| + | The significant rain yield rD(n) of duration D and frequency n [L/s-ha] must be iteratively determined. | ||
| − | + | V<sub>er</sub> = (∑Q<sub>zu</sub> - ∑Q<sub>s</sub>) x D x 60 | |
| − | |||
| − | V<sub>er</sub> = ( | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | The crucial rain yield rD(n), the duration D and frequency n [L/sha] must be determined iteratively. |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Overflow frequency== | ||
| + | For statistical determination of rainwater outflows, the assumed frequency of rain from the rain yield curve is crucial. This value depends on the economic importance of the area and is related to the frequency with which the proposed system is congested. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Frequency of dimensioning system (once in n years) !! Location |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 in 1 || | + | | 1 in 1 || Rural area |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 in 2 || | + | | 1 in 2 || Residential area |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 in 2 || | + | | 1 in 2 || City centers, industrial and commercial areas with flood assessment |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 in 5 || | + | | 1 in 5 || City centers, industrial and commercial areas without flood assessment |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 in 10 || | + | | 1 in 10 || Underground traffic infrastructure, subways |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Source: ATV A118 | |
| − | == | + | ==Flood verification DIN 1986-100:2016-09 (Germany)== |
| − | + | Drainage systems for the discharge of precipitation water from small properties, so long as the sewer network provider has given no other guideline, without a more effective run-off surface, are sufficient for DN 150 connection to the sewer. The rule applies in the same sense to infiltration systems designed according to DWA-A 138 with T = 5 a and a dimensioning rainfall according to KOSTRA-DWD-2010. It is assumed that due to terrain condition and architectural building plans no backed-up water from the system will penetrate into the connected or neighbouring buildings and exceed any other official regulations. | |
| − | + | Ground conduits from properties, according to DIN EN 752 from 200 ha A<sub>ges</sub> i.e. from approximately 60 ha A<sub>E,b</sub>, that drain larger, harmless flood-prone yard, park or other outdoor systems can be designed according to DWA-A 118:2006, Table 4. Here the yearly occurance of the dimensioning rainfall cannot be less once within two years. | |
| − | + | Shortest normative rain period in relation to terrain slope and degree of sealing: | |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center" | ||
| − | |<b> | + | |<b>average terrain slope</b> |
| − | |<b> | + | |<b>Sealing</b> |
| − | |<b> | + | |<b>shortest rain period</b> |
| − | ( | + | (according to this norm r<sub>2</sub> in min) |
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"|< 1% | |rowspan="2"|< 1% | ||
| Zeile 398: | Zeile 434: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Source: DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4 | |
| − | + | For the difference in the amount of rainwater accumulated on a sealed surface of a property, V<sub>Rück</sub> in m³ (see Equation 20), between the minimum 30-year rain event and the 2-year dimensioning rain, proof of harmless flooding on the property must be provided. If an exceptional level of safety is required, the yearly occurance of the dimensioning rain is chosen as greater than 30 a. The harmless flooding can take place on the property, e.g. with curbs or troughs, or through other retention areas, like retention basins, if people, animals or material goods are not endangered, so long as the precipitation water is not discharged on other fields. The following flood verification for guidance is dependent on the local conditions and if necessary for parts of the drainage system (e.g. in the calming areas). | |
| − | === | + | ===Equation 20=== |
| − | '''V<sub>rück</sub> = ( r(D,30) x A<sub>ges</sub> – ( r(D,2) x C<sub>Dach</sub> + r(D,2) x A<sub>FaG</sub> x C<sub>FaG</sub>)) x D x 60 / ( | + | '''V<sub>rück</sub> = (r(D,30) x A<sub>ges</sub> – ( r(D,2) x C<sub>Dach</sub> + r(D,2) x A<sub>FaG</sub> x C<sub>FaG</sub>)) x D x 60 / (10,000 x 1000)''' |
| − | V<sub>Rück</sub> | + | V<sub>Rück</sub> the to-be retained rainwater amount, m³ |
| − | r<sub>(D,2)</sub> | + | r<sub>(D,2)</sub> rain event with period D and 30-year return time |
| − | D | + | D the shortest normative rain period, min, for the dimensioning of drainage outside of a building according to DWA-A-118, Table 4, usually D = 5 min |
| − | C | + | C the run-off coefficient |
| − | A<sub>Dach</sub> | + | A<sub>Dach</sub> the total building roof area, m² |
| − | A<sub>FaG</sub> | + | A<sub>FaG</sub> the total sealed surface outside of the building, m² |
| − | A<sub>ges</sub> | + | A<sub>ges</sub> the total sealed surface oft he property, m², hence A<sub>ges</sub> = A<sub>Dach</sub> + A<sub>FaG</sub> |
| − | + | If the ground conduits are dimensioned according to DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4, then the dimensioning discharge, usually larger, instead can be set according to Equation (21) for the maximum discharge of the ground conduits at full charge Q<sub>voll</sub>: | |
| − | === | + | ===Equation 21=== |
| − | '''V<sub>rück</sub> = (( r<sub>(D,30)</sub>) x A<sub>ges</sub>/ 1000)– Q<sub>voll</sub> x D x 60/1000''' | + | '''V<sub>rück</sub> = ((r<sub>(D,30)</sub>) x A<sub>ges</sub>/ 1000)– Q<sub>voll</sub> x D x 60/1000''' |
| − | V<sub>Rück</sub> | + | V<sub>Rück</sub> the to-be retained rainwater amount, m³ |
| − | D D = 5, 10 | + | D D = 5, 10 and 15 minutes. The larger of these three values is normative for V<sub>Rück</sub>* |
| − | Q<sub>voll</sub> max. | + | Q<sub>voll</sub> max. discharge of the ground conduits at full charge, L/s |
| − | A<sub>ges</sub> | + | A<sub>ges</sub> the total sealed surface of the property, m², hence A<sub>ges</sub> = A<sub>Dach</sub> + A<sub>FaG</sub> |
| − | + | Should the rain catchment surfaces of the property be mostly roof areas and not harmless, flood-prone surfaces (e.g. > 70 %, here as well inner courtyards), the flood verification is demonstrated in connection with emergency drainage of a 5-min, 100-year rain event (r<sub>(5,100)</sub>). | |
| − | + | In the case of limited loading, in addition to the flood verification, the calculation of the required retention volume (Rain Retention Area (RRA)) must be carried out with the „simplest procedure“ in accordance with DWA-A 117. For simplicity’s sake, it is assumed that the yearly occurance T of the dimensioning rain (uniform in relation to the total effective property area) corresponds to the permissible exceedance frequency of the RRA. The loading restriction must include the throttle discharge, L/s and the yearly occurance T of the permitted excess. | |
| − | + | For the calculation of volume related dimensioning exercises, such as the dimensioning of precipitation water retention areas, the mean discharge coefficients C<sub>m</sub> according to Table 9 are to be used to determine the effective area. | |
| − | + | The dimensioning of rain retention areas must considered according to DWA-A 117:2013 for the run-off entering the drainage system in relation to both the sealed area A<sub>E,b</sub> as well as from the non-sealed area (Table 9, No. 3) from inlet to outlet in the drainage system. The determined surface types will be simply called A<sub>FaG</sub> in this norm, with the mean run-off coefficients C<sub>m</sub> multiplied and linked to the calculated value A<sub>u</sub>. | |
| − | + | The required storage volume V<sub>RRR</sub> will be determined according to the maximum difference between the rainfall amount and the discharge volume through the throttle in a specific time period. | |
| − | In | + | In accordance with DWA-A 117, Equation (22) applies for property drainage systems for the design of retention areas (RRA). |
| − | === | + | ===Equation 22=== |
| − | '''V<sub> | + | '''V<sub>RRA</sub> = A<sub>u</sub> x r<sub>D,T</sub> / 10,000 x D x F<sub>z</sub> x 0.06 – D x f<sub>z</sub> x Q<sub>Dr</sub> x 0.06''' |
| − | + | Equation 22 cooresponds to the calculation of the required retention volume related to the inlet restriction according to DWA-A 117 using the „simple method“ (see Capital 3.2 [[#Throttle_discharge|Throttle discharge]] for formula). | |
| − | === | + | ===Example calculation to-be retained rainwater amount according to flood verification=== |
| − | + | Location: Aachen Connected catchment surfaces: Building surfaces: A<sub>Dach</sub> = 1,250 m², pitched tiled roof C<sub>Dach</sub> = 0.8 Catchment surfaces outside of the building: A<sub>FaG</sub> = 4,445 m², asphalt, C<sub>FaG</sub> = 0.9 Total sealed surface of the property: A<sub>ges</sub> = 5,695 m² (A<sub>red</sub> = 5,000 m²) Medium terrain slope: < 1% sealing: > 50 % | |
| − | ==== | + | ====Calculation according to Equation 20==== |
| − | V<sub>rück</sub> = ( r<sub>(D,30)</sub> x A<sub>ges</sub> – ( r<sub>(D,2)</sub> x C<sub>Dach</sub> + r<sub>(D,2)</sub> x A<sub>FaG</sub> x C<sub>FaG</sub>)) x D x 60 / (10000 x 1000) | + | V<sub>rück</sub> = (r<sub>(D,30)</sub> x A<sub>ges</sub> – (r<sub>(D,2)</sub> x C<sub>Dach</sub> + r<sub>(D,2)</sub> x A<sub>FaG</sub> x C<sub>FaG</sub>)) x D x 60 / (10000 x 1000) |
| + | |||
| + | with: D = 10 Min (from DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4) | ||
| − | ==== | + | r<sub>(D,30)</sub> = 273 L/sha r<sub>(D,2)</sub> = 148 L/sha V<sub>rück</sub> = 273 x 5,695 – (148 x 1,250 x 0.8 + 148 x 4,445 x 0.9) x 10 x 60 / (10,000 x 1000) = 48.9 m³ |
| − | + | ====Calculation according to Equation 21==== | |
| − | = | + | V<sub>rück</sub> = ((r<sub>(D,30)</sub> x A<sub>ges</sub> / 10,000) – Q<sub>voll</sub>) x D x 60 /1000 |
| − | + | With: single verification of the dimensioning rainfall quantity: | |
| − | = | + | a) r<sub>(5.30)</sub> = 377 L/sha (from DIN 1986-100, Table A.1 Rain Quantity in Germany) |
| − | + | b) r<sub>(10.30)</sub> = 273 L/sha | |
| − | == | + | c) r<sub>(15.30)</sub> = 223 L/sha Q<sub>voll</sub> = 100.0 L/s |
| − | + | a) V<sub>rück</sub> = ((377 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0) x 5 x 60 / 1000 = 34.4 m³ | |
| − | : | + | b) V<sub>rück</sub> = ((273 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0 ) x 10 x 60 / 1000 = 33.3 m³ |
| − | :A<sub>red</sub> = 100 m² | + | |
| − | : | + | c) V<sub>rück</sub> = ((223 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0 ) x 15 x 60 / 1000 = 24.3 m³ |
| − | :k<sub>f</sub> = 1*10 | + | |
| − | :s<sub>rr</sub> = 0 | + | The larger of the three values V<sub>rück</sub> is normative. |
| − | :f<sub>z</sub> = 1 | + | |
| + | ====Calculation according to Equation 22==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The impounding volume from the standard calculation (according to the inlet limitation) results from Cap. [[#Calculation_example_of_required_storage_volume|3.2.4]] as 41.8 m³. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Conclusion:==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This resulting larger volume is relevant for the calculations for flood verification and the inlet limitation. The relevant size of the retention space is calculated from Equation 18 as 48.9 m³. With this based on the flood verification, the required retention volume is increased by 7.1 m³ (17%). At the latest when the flood volume cannot be represented on the surface then the underground storage volumes must be constructed larger. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sample calculations for infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''a) with value D = 15min and n = 0.2 = Example for various international regions'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Location: Aachen | ||
| + | :A<sub>red</sub>= 100 m² | ||
| + | :Measured rainfall: r15,n=0.2 = 152.6 L/(sha) | ||
| + | :k<sub>f</sub> = 1*10-4 m/s (medium sand) | ||
| + | :s<sub>rr</sub> = 0.56 (DRAINMAX Tunnel installation according to German Institute for Civil Engineering) | ||
| + | :f<sub>z</sub> = 1.1 | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Sample calculation for INTEWA DRAINMAX Tunnel in gravel bed:'' |
| − | :B = 1 | + | :B = 1.85 m, H = 1 m, L = 2.25 m |
| − | :L<sub>erf,rigole</sub> = 1 | + | :L<sub>erf,rigole</sub> = 1.31 m |
| − | :V<sub>erf,rigole</sub> = 1 | + | :V<sub>erf,rigole</sub> = 1.36 m³ (= B x H x L<sub>erf,rigole</sub> x s<sub>rr</sub> = 1.85 m x 1 m x 1.31 m x 0.56) |
| − | : | + | :Required number of DRAINMAX Tunnels: LL<sub>erf,rigole</sub> / L = 0.82 |
| − | ''b) | + | ''b) With iteration = Example for Germany'' |
| − | : | + | :Location: Aachen |
:A<sub>red</sub> = 100 m² | :A<sub>red</sub> = 100 m² | ||
| − | : | + | :Measured rainfall: r<sub>15, n=0.2</sub> = 152.6 l/(s*ha) |
| − | :k<sub>f</sub> = 1*10<sup>-4</sup> m/s ( | + | :k<sub>f</sub> = 1*10<sup>-4</sup> m/s (medium sand) |
{| class="wikitable" "text-align:rechts" | {| class="wikitable" "text-align:rechts" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Duration D [min] !! Rain yeld r [L/sha] !! L<sub>erf,rigole</sub> [m] !! V<sub>erf,rigole</sub> [m³] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 5 || 243 | + | | 5 || 243.00 || 0.75 || 0.77 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 10 || 183 | + | | 10 || 183.90 || 1.09 || 1.13 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 15 || 152 | + | | 15 || 152.60 || 1.31 || 1.36 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 20 || 131 | + | | 20 || 131.70 || 1.46 || 1.51 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 30 || 104 | + | | 30 || 104.80 || 1.64 || 1.69 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 45 || 81 | + | | 45 || 81.20 || 1.74 || 1.80 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | '''60''' || '''66 | + | | '''60''' || '''66.80''' || '''1.76''' || '''1.83''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 90 || 49 | + | | 90 || 49.70 || 1.70 || 1.76 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 120 || 40 | + | | 120 || 40.30 || 1.62 || 1.68 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 180 || 29 | + | | 180 || 29.90 || 1.46 || 1.51 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 240 || 24 | + | | 240 || 24.30 || 1.33 || 1.38 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 360 || 18 | + | | 360 || 18.00 || 1.12 || 1.16 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 540 || 13 | + | | 540 || 13.40|| 0.91 || 0.95 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 720 || 10 | + | | 720 || 10.90 || 0.78 || 0.81 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1080 || 7 | + | | 1080 || 7.90 || 0.60 || 0.62 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1440 || 6 | + | | 1440 || 6.50 || 0.51 || 0.52 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2880 || 3 | + | | 2880 || 3.70 || 0.3 || 0.31 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 4320 || 2 | + | | 4320 || 2.90 || 0.24 || 0.25 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | ''c. | + | ''c. Table for rough estimation of small systems with r<sub>15,n=0.2</sub>'' |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! k<sub>f</sub> (m/s) !! !! colspan="3"| | + | ! k<sub>f</sub> (m/s) !! !! colspan="3"| e.g. location Aachen (D) r<sub>15,0.2</sub>=152.6 L/sha!! colspan="3"|e.g. location Berlin (D) r<sub>15,0.2</sub>=213.1 L/sha |
|- | |- | ||
| || || A=100 m<sup>2</sup> || A=150 m<sup>2</sup> || A=200 m<sup>2</sup> || A=100 m<sup>2</sup> || A=150 m<sup>2</sub> || A=200 m<sup>2</sup> | | || || A=100 m<sup>2</sup> || A=150 m<sup>2</sup> || A=200 m<sup>2</sup> || A=100 m<sup>2</sup> || A=150 m<sup>2</sub> || A=200 m<sup>2</sup> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1*10<sup>-4</sup> || | + | | 1*10<sup>-4</sup> || Volume in m<sup>3</sup> || 1.36 || 2.04 || 2.72 || 1.90 || 2.85 || 3.79 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1*10<sup>-5</sup> || | + | | 1*10<sup>-5</sup> || Volume in m<sup>3</sup> || 1.49 || 2.24 || 2.99 || 2.09 || 3.13 || 4.79 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1*10<sup>-6</sup> || | + | | 1*10<sup>-6</sup> || Volume in m<sup>3</sup> || 1.51 || 2.26 || 3.02 || 2.11 || 3.16 || 4.21 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Rough estimation of retention volume== |
| − | + | The following method of calculation can be used for a rough estimation of required retention volume with specified rain duration. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Example calculation:''' |
| − | : | + | :Permitted discharge from property: 1.5 L/sha |
| − | : | + | :Property size: 0.105 ha |
| − | : | + | :Rain yield r<sub>15(1)</sub> = 108 L/sha |
| − | : | + | :Rain yield r<sub>15(2)</sub> = 193 L/sha |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Surface !! x !! Runoff coefficient !! x !! Rain yield !!= !! Q<sub>r15(2)</sub> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 231 m<sup>2</sup> || x || 1 || x || 0 | + | | 231 m<sup>2</sup> || x || 1 || x || 0.0193 L/s x m<sup>2</sup> || = || 4.46 L/s |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 114 m<sup>2</sup> || x || 0 | + | | 114 m<sup>2</sup> || x || 0.8 || x || 0.0193 L/s x m<sup>2</sup> || = || 1.76 L/s |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Total rainwater runoff || || || ||Q<sub>rges</sub> || = || 6.22 L/s |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2"| | + | | colspan="2"| Approved discharge quantity: || Q<sub>ab</sub> ||=|| colspan="3"|0.105 ha (property size) x 1.5 L/sha |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="3"| || = || colspan="3"|0 | + | | colspan="3"| || = || colspan="3"|0.158 L/s |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2"| | + | | colspan="2"|Rainwater quantity for retention: || Q<sub>s</sub> ||=|| colspan="3"|Q<sub>r15(0.2)ges</sub> - Q<sub>ab</sub> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="3"| || = || colspan="3"|6 | + | | colspan="3"| || = || colspan="3"|6.22 L/s – 0.158 L/s = 6.06 L/s |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="7"| | + | | colspan="7"| Required backwater volume Verf: (The retention system must absorb Qs for 15 min.). |
|- | |- | ||
| Verf ||colspan="6" |= Q<sub>s</sub> x 60 x 15 = Q<sub>s</sub> x 900 | | Verf ||colspan="6" |= Q<sub>s</sub> x 60 x 15 = Q<sub>s</sub> x 900 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | || colspan="6" |= 6 | + | | || colspan="6" |= 6.06 L/s x 900 s = 5.5 m<sup>3</sup> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Accurate dimensioning of a trench or retention system with planning software== |
| − | + | Since calculation of the required trench volume is iterative, planning software such as the [https://www.rainplaner.net/en/ RAINPLANER] is better designed for solving it. | |
| − | == | + | ==Dimensioning surface infiltration== |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan="2"|A<sub>s</sub> = A<sub>red</sub> / ( k<sub>r</sub> x s<sub>f</sub> x 107 / 2 x r <sub>D(n)</sub> –1) | + | ! colspan="2"|A<sub>s</sub> = A<sub>red</sub> / (k<sub>r</sub> x s<sub>f</sub> x 107 / 2 x r <sub>D(n)</sub> –1) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | A<sub>red</sub> || = | + | | A<sub>red</sub> || = connected paved surfaces |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | s<sub>f</sub> || = | + | | s<sub>f</sub> || = Joints proportion in a permeable paved area (0 < s<sub>f</sub> =< 1) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | k<sub>r</sub> || = | + | | k<sub>r</sub> || = Permeability coefficient in the considered infiltration layer |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = | + | | r<sub>D(n)</sub> || = Rain yield |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="2"| | + | !colspan="2"|Example: |
|- | |- | ||
| A<sub>red</sub> || = 300 m<sup>2</sup> | | A<sub>red</sub> || = 300 m<sup>2</sup> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | s<sub>f</sub> || = 1 (INTEWA | + | | s<sub>f</sub> || = 1 (INTEWA grass grid pavers) |
|- | |- | ||
| k<sub>r</sub> || = 2 x 10<sup>-4</sup> m/s | | k<sub>r</sub> || = 2 x 10<sup>-4</sup> m/s | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | r <sub>D(n)</sub> || = | + | | r <sub>D(n)</sub> || = from KOSTRA table with n=0.2/a and D=10 min: r<sub>10(0.2)</sub> = 204.60 L/sha |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="2"|A<sub>s</sub> = 300 / ( 2 x 10<sup>-4</sup> x 1 x 10<sup>7</sup> / 2 x 204 | + | !colspan="2"|A<sub>s</sub> = 300 / ( 2 x 10<sup>-4</sup> x 1 x 10<sup>7</sup> / 2 x 204.6 –1) = 77 m<sup>2</sup> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Dimensioning infiltration trenches behind small wastewater treatment systems== |
| + | |||
| + | According to DIN 4261-1, version 2002, the water discharged from SWWTPs can be infiltrated through trenches in soils with k<sub>f</sub> = 5 x 10<sup>-7</sup> to 5 x 10<sup>-3</sup> m/s. As the base of infiltration system can clog up with time, only the side areas remain effective in the long run. A large retention volume is an advantage for variable infiltration efficiency i.e. during frost or uneven loading of the trench. The following simplified dimensioning methods shall apply according to DIN: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Datei:RWV_rigolenKleinkl.jpg |miniatur| | + | [[Datei:RWV_rigolenKleinkl.jpg|miniatur|400px|Trenches behind small wastewater treatment systems]] |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan="3"| | + | ! colspan="3"| Required wall area (m<sup>2</sup>/inhabitant value PE): |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2"|1 m<sup>2</sup> / | + | | colspan="2"|1 m<sup>2</sup> / PE to 1.5 m<sup>2</sup> / PE with:|| Sand-gravel mixture, sand, light silty sand |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2"|2 m<sup>2</sup> / | + | | colspan="2"|2 m<sup>2</sup> / PE to 2.5 m<sup>2</sup> / PE with:|| Silt (also light clay), sand-silt mixture, stone-loam mixture |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan="3"| | + | ! colspan="3"| Required number for example of DRAINMAX Tunnel: |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Base element || colspan="2"|2.25 m length x 0.8 m heigth x 2 sides |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | A<sub>s</sub> ||colspan="2"|= 3 | + | | A<sub>s</sub> ||colspan="2"|= 3.6 m<sup>2</sup> per tunnel without front walls |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |PE|| to 1.5 m²/PE || to 2.5 m²/PE |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4 || 1 | + | |4 || 1 pcs.|| 2 pcs. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |8 || 1 | + | |8 || 1 pcs.|| 4 pcs. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |12|| 3 | + | |12|| 3 pcs.|| 6 pcs. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |16 || 4 | + | |16 || 4 pcs.|| 8 pcs. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | A specified calculation must be done with other soil conditions and higher PE values. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Comparison between DRAINMAX Tunnel and pipe trench variants''' |
| − | + | According to EN 12566-3 for small wastewater treatment plants (SWWTPs) 150 L / day / inhabitant (PE) has the following daily distribution: | |
3h = 30%<br/> | 3h = 30%<br/> | ||
| Zeile 668: | Zeile 726: | ||
7h = 0%<br/> | 7h = 0%<br/> | ||
| − | + | When using a classic pipe trench, the largest flow rate must be determined. This occurs within 2h with 40%. For a SWWTP with 5 PE this is calculated as follows: | |
| − | 40 % in 2 h | + | 40 % in 2 h from 750 L/day<br/> |
| − | => 300 | + | => 300 L/2h<br/> |
| − | => 0 | + | => 0.0417 L/s<br/> |
| − | + | When using the DRAINMAX Tunnel, the daily volume can be stored in the trench. The largest flow rate is then calculated as follows: | |
| − | 100 % in 24 h | + | 100 % in 24 h from 750 L/day<br/> |
| − | => 750 | + | => 750 L/24 h<br/> |
| − | => 0 | + | => 0.0087 L/s<br/> |
| − | => | + | => this flow rate is 4.8 times smaller than with the pipe trench variant<br/> |
| − | => | + | => the DRAINMAX tunnel can be dimensioned approx. 4.8 times smaller than the pipe trench<br/> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | = | + | =Legal framework conditions in Germany= |
| − | + | When planning and installing an infiltration or retention system, the current versions of the following regulations must be observed: | |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:rechts" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:rechts" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Scope !! Policy !! Content |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="9" | ''' | + | | rowspan="9" | '''Water supply''' |
| − | | Arbeitsblatt DWA-A 138 || | + | | Arbeitsblatt DWA-A 138 || Planning, construction and operation of precipitation water infiltration systems |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ATV-DVWK-M 153 || | + | | ATV-DVWK-M 153 || Recommendations for handling rainwater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ATV-A 121 || | + | | ATV-A 121 || local precipitation / heavy rainfall analysis according to return period and duration |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | DWA-A 117 || | + | | DWA-A 117 || Design of rain retention spaces |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Kostra || | + | | Kostra || Heavy precipitation amounts for Germany |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | DIN 4261-1,Kapitel 9 || | + | | DIN 4261-1, Kapitel 9 || Small wastewater treatment plants, transport underground of biologically treated wastewater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | EN 752 || | + | | EN 752 || Drainage outside of buildings… |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ATV A 118 || | + | | ATV A 118 || Hydraulic design and verification of drainage systems |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ATV A 118 || | + | | ATV A 118 || Guidelines for the design of rainwater discharge systems in mixed water sewers |
|} | |} | ||
| − | = | + | =Obligations to notify and obtain license= |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:rechts" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:rechts" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Scope !! Policy !! Content |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="1" | '''EU | + | | rowspan="1" | '''EU legislation''' |
| − | | | + | | Anzeige- und Genehmigungspflichten |
| − | EG- | + | EG-Directive 80/68/EWG / 1979 || Pollution resulting from the discharge of specific dangerous substances into community waters. Protection of groundwater against pollution by specific dangerous substances |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | ''' | + | | rowspan="2" | '''Federal legislation''' |
| − | | | + | | Household water law WHG || In accordance with the WHG, infiltration plants require a licence, since 1996 the States have been able to abolish the licence requirement, |
| + | groundwater regulation | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Building Code || Building Code |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="5" | ''' | + | | rowspan="5" | '''State legislation''' |
| − | | | + | | State Building Regulation || Specification of the type of system and size in the building application, most state building regulations meanwhile promote or demand the decentralized infiltration of precipitation water |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Wastewater Regulation || Request for partial exemption from the obligation to connect and use the public sewage system. Obligation to declare prior to construction of the system at the municipal water utility |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | State Water Law || possible obligation to infiltrate rainwater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | State Water Law || possible permission of the subsidiary water authority for infiltration |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | kommunale Abwassersatzung || | + | | kommunale Abwassersatzung || possible application for partial exemption from connection and compulsory use at the municipal water disposal company |
|} | |} | ||
=Weblinks= | =Weblinks= | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 29. März 2019, 09:27 Uhr
In water management, experience asserts that rainwater should be infiltrated at the place where it accumulates. If this is not possible, then in many cases the temporary storage (attenuation or retention) of rainwater is required in attenuation volumes in order to protect the drainage systems from overloading and to limit their dimension.
Advantages of rainwater infiltration
For end users:
- stormwater fees are saved
- the local microclimate is improved
For municipalities:
- lower costs for flood protection / flood prevention
- lower costs for sewer construction, sewer rehabilitation and sewage plant operation
- lower connection costs for new developments
- protection of the groundwater supply
Advantages of rainwater retention:
- limiting area discharge, reducing flood risk
- lower costs in sewer construction, sewer rehabilitation and sewage plant operation
- connection of new developments to existing, full-capacity drainage systems
- relief of overloaded sewer networks
Basic principles
Quality of rainwater runoff
The runoff from paved surfaces are classified into the categories of non-hazardous, tolerable and intolerable according to their material concentration and thereby possibly associated potential hazards to groundwater in targeted rainwater infiltration.
Non-hazardous rainwater runoff
Non-hazardous rainwater runoff can be infiltrated (e.g. in trenches) without pretreatment measures through the unsaturated zone (below the root zone and above the groundwater level).
Tolerable rainwater runoff
Tolerable rainwater runoff can be infiltrated through the unsaturated zone after suitable pretreatment or using cleaning processes (sedimentation system, rainwater cisterns, overgrown soil, etc.).
Intolerable rainwater runoff
Intolerable rainwater runoff can only be infiltrated after pretreatment.
| Surface / Area | Qualitative evaluation |
|---|---|
| Green roofs, fields and cultivated land; roof surfaces without the use of uncoated metals (copper, zinc and lead), terrace surfaces in residential and similar commercial areas | non-hazardous |
| Roofs with usual proportions of uncoated metals, cycle tracks and footpaths in residential areas, calm traffic areas; lawns and car parking without frequent vehicle changes; as well as lightly used vehicle areas (up to DTV 300 vehicles); streets with DTV 300 - 5,000 vehicles, e.g. access roads, residential and district streets; airport tarmac; roofs in commercial and industrial areas with significant air pollution, see DWA-A138. | tolerable |
| Lawns and streets in commercial and industrial areas with significant air pollution; for special zones see DWA | intolerable |
Source DWA-A138, DTV = average daily traffic intensity
Soil composition
Infiltration capacity of the soil
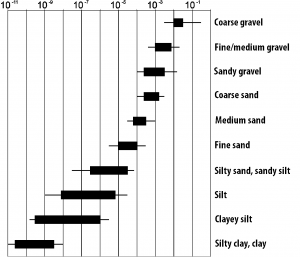
The underground composition is of crucial importance for rainwater infiltration. The permeability coefficient (kf-value) is a measure of water permeability of the soil. The permeability coefficient should be between 10-3 and 10-6 in order to ensure the functionality of the infiltration system.
In order to avoid over-dimensioning of the system, the kf-value should be determined as accurately as possible through investigation. There are professional geotechnical experts for this purpose.
Quick test for soil composition
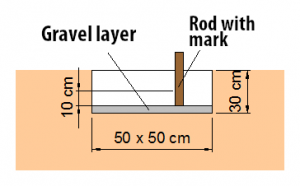
If the kf-value is unknown, then an approximation of the underground infiltration can be isolated based on the following short test.
- Dig a 50 x 50 cm wide and approx. 30 cm deep pit. Important: Do not enter the pit to avoid compression!
- Cover the soil with a gravel layer to prevent soil flotation. Insert a measuring rod into the ground. 10 cm above the pit bottom place a mark on the measuring rod.
- Now fill the pit with water and replenish for 1-2 hours regularly (e.g. garden hose).
- Fill water up to the mark. After 10 minutes, fill as much water as necessary to raise the water level back to the mark using a measuring bucket. The soil permeability can be estimated from the quantity of refilled water.
- Repeat step 4 as many times (at least 3 times), until a consistent value is established.
Evaluation:
Water quantity < 1.5 litres in 10 minutes: little infiltration possible (silt)
Water quantity = 1.5 litres in 10 minutes: infiltration possible (silty sand)
Water quantity > 3 litres in 10 minutes: good infiltration possible (sand, gravel)
Cleaning options for precipitation water
The contamination of underground and surface water from rainwater from roofs and traffic areas can be considered qualitatively and quantitatively by using simple assessment procedures (ATV DVWK-M153). Depending on the result, various measures for handling rainwater must be taken to ensure adequate water protection.
For discharge into a trench, minimum protection requires coarse filtration.
- Important: with rainwater harvesting cisterns
According to DIN 1989-1, underground infiltrations systems (trenches) are equivalent to infiltration systems in active soil areas in terms of qualitative aspects, provided the inlet water comes from a rainwater harvesting system with non-metallic roof areas.
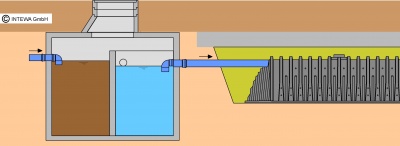
Sedimentation and filter chamber, sedimentation systems
Systems with a settling chamber in which the flow conditions allow specific substances heavier than water sink and specific lighter substances float are referred to as sedimentation systems.
Collection and filter chambers consist of a sedimentation area in which heavy particles settle and a filter that prevents light coarse contaminants from entering the downstream storage. Even light materials are retained in the chamber with an immersion pipe. Depending on the amount of dirt, they must be cleaned regularly. The total water discharged from roof is filtered and supplied to the tank. In Germany the chambers are designed in accordance with ATV DVWK-M153, corresponding to the expected amount of dirt and connected roof area.
Soil passages
Contaminants from flowing rainwater are retained and stored or degraded by physical, chemical and if necessary, biological processes with passage through soil layers or in trough-trench systems or unsealed surfaces such as grass pavers. Thus passage through overgrown topsoil is more effective than through a non-vegetated soil zone. The protective cover layers over groundwater must not be penetrated.
Flushable and camera-accessible trenches
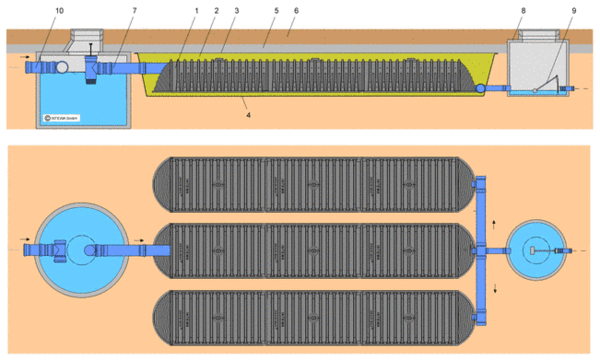
Should contaminants penetrate into the trench despite pre-cleaning, it is very important that subsequent cleaning is possible. In many trenches e.g. box systems, only the flushing ducts can be cleaned afterwards. However fine contaminates pass through the slots in the flushing ducts and gradually clog the floors and walls of these trenches. Ultimately these can only be dug out completely if they have lost their infiltration capacity. With DRAINMAX Tunnel trenches for example, the critical walls and floors can be inspected with a camera through adequate connection chambers and are completely flushable. Contaminants either are retained in the coarse filter of the sedimentation and filter chamber or settle in the sedimentation area. The coarse filter can be removed and emptied after the flushing process. The parallel rows of trenches are additionally protected by the long settling section in the seepage pipe and the additional settling possibility in the inspection and flushing chamber. This guarantees a constant infiltration performance long-term.
Construction of an infiltration system
- Distance to MHGW (mean highest groundwater level) from the bottom of the system: > 1 m
- Soil permeability > 1 x 10-6 (with lower values see retention)
- Soil permeability < 1 x 10-3 (with higher permeability too little treatment)
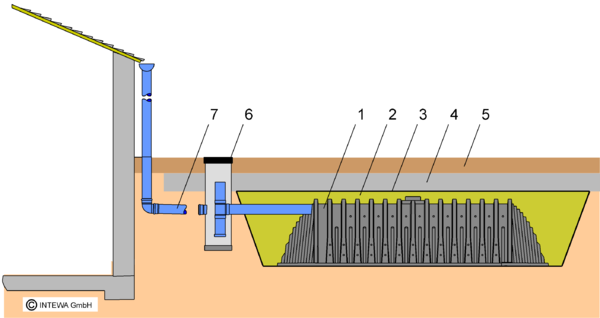
Trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel
| 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel | 5. Topsoil |
| 2. Tunnel side and top backfill | 6. Sedimentation/filter chamber |
| 3. Geotextile | 7. Rainwater inlet |
| 4. Tunnel overburden |
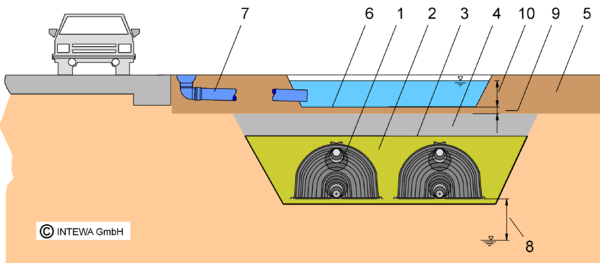
Trough-trench infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel
| 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel | 6. Infiltration trough |
| 2. Tunnel side and top backfil | 7. Rainwater inlet |
| 3. Geotextile | 8. Distance to groundwater |
| 4. Tunnel overburden | 9. Active soil zone |
| 5. Topsoil | 10. Maximum water level |
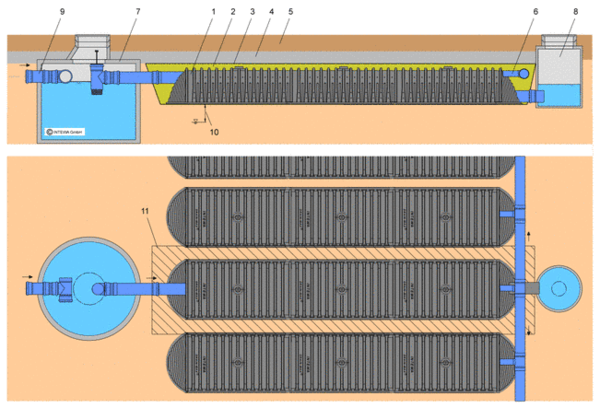
DRAINMAX Tunnel System for commercial properties
| 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel | 7. Sedimentation/filter chamber |
| 2. Tunnel side and top backfill | 8. Flushing chamber |
| 3. Geotextile | 9. Rainwater inlet |
| 4. Tunnel overburden | 10. Maximum water level |
| 5. Topsoil | 11. Geotextile composite bottom layer |
| 6. Rainwater distribution |
Construction of a retention system
Retention volume
There are several options for the retention of rainwater:
- Storage with pure retention and throttle discharge
- Storage with combined retention and use and throttle discharge
The combination of rainwater harvesting and rainwater retention in a cistern is particularly interesting for smaller systems for single-family homes since the costs for excavation and delivery are incurred only once and the cistern is not significantly more expensive.
- Retention with approved partial infiltration and throttle discharge
With permitted partial infiltration, the DRAINMAX system with tunnel elements is an extremely interesting alternative. The low height offset between inlet and outlet in combination with large space flexibility and a very high storage volume are the advantages of this variant. If no water is allowed to enter the surrounding soil from the system, it can be sealed with an EPDM foil on site.
| 1. DRAINMAX Tunnel | 6. Topsoil |
| 2. Tunnel side and top backfill | 7. Sedimentation/filter chamber |
| 3. Geotextile | 8. Throttle chamber |
| 4. Enclosed sheet basin made from EPDM and geotextile | 9. Discharge throttle |
| 5. Tunnel overburden | 10. Rainwater inlet |
Throttle discharge
In a retention system the water is supplied into the drainage system with a throttled flow rate. The throttle discharge corresponds to the permitted outflow of the sealed area connected to the drainage system. Most of the time this discharge corresponds to the natural flow before sealing the area.
In the retention system the permissible throttle discharge is either supplied to a downstream drainage system by means of a lift pump or through a discharge throttle provided the height conditions allow. According to DWA-A 117, the arithmetic average of the values of the throttle curve is to be set for uncontrolled throttling (fixed throttle/vortex throttle).
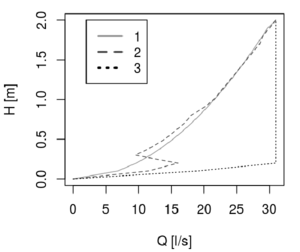
Compared to the vortex or fixed throttle, continuous throttles make sure that the maximum permitted water quantity Q drains constantly, irrespective of the impounding depth H. As a result, the retention tank with continuous throttle can be dimensioned by 10% to 30% smaller than with fixed throttle discharge or vortex throttles.
Exp. throttle curve for maximum admissible water quantity of 31 L/s
1. Fixed throttle (arithmetic mean = 21 L/s)
2. Vortex throttle (arithmetic mean = 21 L/s)
3. Continuous discharge throttle (31 L/s)
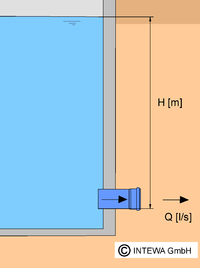
Fixed throttle
The simplest form of a fixed or static throttle is a simple flow restrictor. The discharge value Q of the fixed throttle depends on the hydrostatic pressure resulting from the impounding depth H.
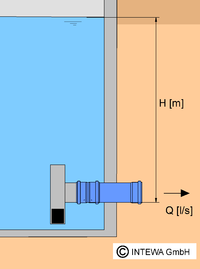
Vortex throttle
A spiral stream of variable strength with a central rotating air core is formed by the tangential feed in the vortex throttle depending on the water level. However this does not lead to a continuous throttle outflow. The vortex throttle has the advantage of requiring less space and lower risk of blockages due to the larger remaining cross-section compared to the other throttle types. These advantages are rarely relevant with decentralized rainwater retention.
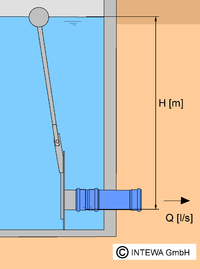
Continuous throttle
The outlet flow is constant with the continuous discharge throttle irrespective of the impounding depth H. The float adjusts the restrictor opening at the impounding depth by means of a lever arm. Coarse pre-cleaning of rainwater is necessary for the trouble-free operation of the throttle.
Calculation example of required storage volume
The crucial rain yield rD(n), the duration D and frequency n [L/s-ha] must be determined iteratively (see Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems).
| Verf = ((Ared x rD(n) x 10-4) – Qdr ) x D x 60 x 10-3 | |
| Verf | = required storage volume in m³ |
| Ared | = connected paved surfaces in m² (5,000 m² in example) |
| rD(n) | = crucial rainfall in L/sha (e.g. KOSTRA-Data Aachen, see Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems) |
| Qdr | = discharge throttle value in L/s (the arithmetic mean of the throttle curve with non-continuous throttles, see diagram of throttle curves, 21 L/s in the example) |
| D | = Duration in min (in example, 30 min with the fixed throttle and vortex throttle, 20 min with the continuous throttle) |
| fixed throttle = vortex throttle: Verf = ((5,000 x 104.8 x 10-4) – 21) x 30 x 60 x 10-3 = 56.6 m³ | |
| continuous throttle: Verf = ((5,000 x 131.7 x 10-4) – 31) x 20 x 60 x 10-3 = 41.8 m³ (- 26 %) | |
The larger the permitted throttle outflow in relation to the connected areas, the greater the difference. This difference leads to correspondingly lower total costs for the retention system.
Dimensioning of infiltration or retention systems
Also see Online Planner
Rainwater runoff
The calculation of rainwater runoff is based on the knowledge that heavy rains last short durations and low rains persist for longer. The rainfall yield declines at the same statistical frequency with increasing rainfall duration. The relationship between rainfall yield, duration and frequency is determined by the statistical analysis of precipitation registrations. Simple calculation methods in Germany are used in accord with DWA-A 117. For this a statistical rainfall with selected duration D and frequency n should be used as load case for calculation. For the determination of rain yield refer to the "amount of heavy peak rainfall in Germany - KOSTRA" (see table for a sample location).
| Rain duration D | r D(1) l/(sha) | r D(0,2) l/(sha) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 135.0 | 243.0 |
| 10 min | 113.0 | 183.9 |
| 15 min | 97.2 | 152.6 |
| 20 min | 85.3 | 131.7 |
| 30 min | 69.5 | 104.8 |
| 45 min | 52.9 | 81.2 |
| 60 min | 43.1 | 66.8 |
| 90 min | 32.3 | 49.7 |
| 2 h | 26.4 | 40.3 |
| 3 h | 19.8 | 29.9 |
| 4 h | 16.1 | 24.3 |
| 6 h | 12.1 | 18.0 |
| 9 h | 9.1 | 13.4 |
| 12 h | 7.4 | 10.9 |
| 18 h | 5.4 | 7.9 |
| 24 h | 4.3 | 6.5 |
| 48 h | 2.6 | 3.7 |
| 72 h | 2.1 | 2.9 |
KOSTRA data sample location
Inflow to infiltration or retention systems
- Qzu = 10-7 x rD(n) x Ared (1.)
| Qzu | = Inflow to infiltration system in m³/s |
| rD(n) | = Rain yield for duration D and frequency n [L/sha] |
| Ared | = connected paved areas in m² |
Discharge from the infiltration system
Darcy’s Law is used to calculate the discharge from an infiltration system:
- Qs = (b+0,5h) x L x ½ x kf (2.a)
| kf | = Permeability coefficient of the saturated soil in m/s |
| b | = Bottom width of the trench in m |
| h | = Height of the trench in m |
| L | = Length of the trench in m |
Discharge from the retention system
Continuity condition
- Verf = L x b x h x sRR = (∑Qzu - ∑Qs) x D x 60 (3.)
| Verf | = required storage volume in m³ |
| D | = Rain duration in min |
Infiltration: If only formulas 1. and 2.a are used for formula 3 to calculate L, then this will result in a significant trench length and volume.
SRR = Storage coefficient of the trench
Retention: Here, only formulas 1. and 2.b are used in formula 3. Ver = (∑Qzu - ∑Qs) x D x 60 The significant rain yield rD(n) of duration D and frequency n [L/s-ha] must be iteratively determined.
Ver = (∑Qzu - ∑Qs) x D x 60
The crucial rain yield rD(n), the duration D and frequency n [L/sha] must be determined iteratively.
Overflow frequency
For statistical determination of rainwater outflows, the assumed frequency of rain from the rain yield curve is crucial. This value depends on the economic importance of the area and is related to the frequency with which the proposed system is congested.
| Frequency of dimensioning system (once in n years) | Location |
|---|---|
| 1 in 1 | Rural area |
| 1 in 2 | Residential area |
| 1 in 2 | City centers, industrial and commercial areas with flood assessment |
| 1 in 5 | City centers, industrial and commercial areas without flood assessment |
| 1 in 10 | Underground traffic infrastructure, subways |
Source: ATV A118
Flood verification DIN 1986-100:2016-09 (Germany)
Drainage systems for the discharge of precipitation water from small properties, so long as the sewer network provider has given no other guideline, without a more effective run-off surface, are sufficient for DN 150 connection to the sewer. The rule applies in the same sense to infiltration systems designed according to DWA-A 138 with T = 5 a and a dimensioning rainfall according to KOSTRA-DWD-2010. It is assumed that due to terrain condition and architectural building plans no backed-up water from the system will penetrate into the connected or neighbouring buildings and exceed any other official regulations.
Ground conduits from properties, according to DIN EN 752 from 200 ha Ages i.e. from approximately 60 ha AE,b, that drain larger, harmless flood-prone yard, park or other outdoor systems can be designed according to DWA-A 118:2006, Table 4. Here the yearly occurance of the dimensioning rainfall cannot be less once within two years.
Shortest normative rain period in relation to terrain slope and degree of sealing:
| average terrain slope | Sealing | shortest rain period
(according to this norm r2 in min) |
| < 1% | ≤ 50% | 15 min |
| > 50% | 10 min | |
| 1% bis 4% | - | 10 min |
| > 4% | ≤ 50% | 10 min |
| > 50% | 5 min |
Source: DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4
For the difference in the amount of rainwater accumulated on a sealed surface of a property, VRück in m³ (see Equation 20), between the minimum 30-year rain event and the 2-year dimensioning rain, proof of harmless flooding on the property must be provided. If an exceptional level of safety is required, the yearly occurance of the dimensioning rain is chosen as greater than 30 a. The harmless flooding can take place on the property, e.g. with curbs or troughs, or through other retention areas, like retention basins, if people, animals or material goods are not endangered, so long as the precipitation water is not discharged on other fields. The following flood verification for guidance is dependent on the local conditions and if necessary for parts of the drainage system (e.g. in the calming areas).
Equation 20
Vrück = (r(D,30) x Ages – ( r(D,2) x CDach + r(D,2) x AFaG x CFaG)) x D x 60 / (10,000 x 1000)
VRück the to-be retained rainwater amount, m³
r(D,2) rain event with period D and 30-year return time
D the shortest normative rain period, min, for the dimensioning of drainage outside of a building according to DWA-A-118, Table 4, usually D = 5 min
C the run-off coefficient
ADach the total building roof area, m²
AFaG the total sealed surface outside of the building, m²
Ages the total sealed surface oft he property, m², hence Ages = ADach + AFaG
If the ground conduits are dimensioned according to DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4, then the dimensioning discharge, usually larger, instead can be set according to Equation (21) for the maximum discharge of the ground conduits at full charge Qvoll:
Equation 21
Vrück = ((r(D,30)) x Ages/ 1000)– Qvoll x D x 60/1000
VRück the to-be retained rainwater amount, m³
D D = 5, 10 and 15 minutes. The larger of these three values is normative for VRück*
Qvoll max. discharge of the ground conduits at full charge, L/s
Ages the total sealed surface of the property, m², hence Ages = ADach + AFaG
Should the rain catchment surfaces of the property be mostly roof areas and not harmless, flood-prone surfaces (e.g. > 70 %, here as well inner courtyards), the flood verification is demonstrated in connection with emergency drainage of a 5-min, 100-year rain event (r(5,100)).
In the case of limited loading, in addition to the flood verification, the calculation of the required retention volume (Rain Retention Area (RRA)) must be carried out with the „simplest procedure“ in accordance with DWA-A 117. For simplicity’s sake, it is assumed that the yearly occurance T of the dimensioning rain (uniform in relation to the total effective property area) corresponds to the permissible exceedance frequency of the RRA. The loading restriction must include the throttle discharge, L/s and the yearly occurance T of the permitted excess. For the calculation of volume related dimensioning exercises, such as the dimensioning of precipitation water retention areas, the mean discharge coefficients Cm according to Table 9 are to be used to determine the effective area. The dimensioning of rain retention areas must considered according to DWA-A 117:2013 for the run-off entering the drainage system in relation to both the sealed area AE,b as well as from the non-sealed area (Table 9, No. 3) from inlet to outlet in the drainage system. The determined surface types will be simply called AFaG in this norm, with the mean run-off coefficients Cm multiplied and linked to the calculated value Au. The required storage volume VRRR will be determined according to the maximum difference between the rainfall amount and the discharge volume through the throttle in a specific time period.
In accordance with DWA-A 117, Equation (22) applies for property drainage systems for the design of retention areas (RRA).
Equation 22
VRRA = Au x rD,T / 10,000 x D x Fz x 0.06 – D x fz x QDr x 0.06
Equation 22 cooresponds to the calculation of the required retention volume related to the inlet restriction according to DWA-A 117 using the „simple method“ (see Capital 3.2 Throttle discharge for formula).
Example calculation to-be retained rainwater amount according to flood verification
Location: Aachen Connected catchment surfaces: Building surfaces: ADach = 1,250 m², pitched tiled roof CDach = 0.8 Catchment surfaces outside of the building: AFaG = 4,445 m², asphalt, CFaG = 0.9 Total sealed surface of the property: Ages = 5,695 m² (Ared = 5,000 m²) Medium terrain slope: < 1% sealing: > 50 %
Calculation according to Equation 20
Vrück = (r(D,30) x Ages – (r(D,2) x CDach + r(D,2) x AFaG x CFaG)) x D x 60 / (10000 x 1000)
with: D = 10 Min (from DWA-A-118:2006, Table 4)
r(D,30) = 273 L/sha r(D,2) = 148 L/sha Vrück = 273 x 5,695 – (148 x 1,250 x 0.8 + 148 x 4,445 x 0.9) x 10 x 60 / (10,000 x 1000) = 48.9 m³
Calculation according to Equation 21
Vrück = ((r(D,30) x Ages / 10,000) – Qvoll) x D x 60 /1000
With: single verification of the dimensioning rainfall quantity:
a) r(5.30) = 377 L/sha (from DIN 1986-100, Table A.1 Rain Quantity in Germany)
b) r(10.30) = 273 L/sha
c) r(15.30) = 223 L/sha Qvoll = 100.0 L/s
a) Vrück = ((377 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0) x 5 x 60 / 1000 = 34.4 m³
b) Vrück = ((273 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0 ) x 10 x 60 / 1000 = 33.3 m³
c) Vrück = ((223 x 5,695 / 10,000) – 100.0 ) x 15 x 60 / 1000 = 24.3 m³
The larger of the three values Vrück is normative.
Calculation according to Equation 22
The impounding volume from the standard calculation (according to the inlet limitation) results from Cap. 3.2.4 as 41.8 m³.
Conclusion:
This resulting larger volume is relevant for the calculations for flood verification and the inlet limitation. The relevant size of the retention space is calculated from Equation 18 as 48.9 m³. With this based on the flood verification, the required retention volume is increased by 7.1 m³ (17%). At the latest when the flood volume cannot be represented on the surface then the underground storage volumes must be constructed larger.
Sample calculations for infiltration with DRAINMAX Tunnel
a) with value D = 15min and n = 0.2 = Example for various international regions
- Location: Aachen
- Ared= 100 m²
- Measured rainfall: r15,n=0.2 = 152.6 L/(sha)
- kf = 1*10-4 m/s (medium sand)
- srr = 0.56 (DRAINMAX Tunnel installation according to German Institute for Civil Engineering)
- fz = 1.1
Sample calculation for INTEWA DRAINMAX Tunnel in gravel bed:
- B = 1.85 m, H = 1 m, L = 2.25 m
- Lerf,rigole = 1.31 m
- Verf,rigole = 1.36 m³ (= B x H x Lerf,rigole x srr = 1.85 m x 1 m x 1.31 m x 0.56)
- Required number of DRAINMAX Tunnels: LLerf,rigole / L = 0.82
b) With iteration = Example for Germany
- Location: Aachen
- Ared = 100 m²
- Measured rainfall: r15, n=0.2 = 152.6 l/(s*ha)
- kf = 1*10-4 m/s (medium sand)
| Duration D [min] | Rain yeld r [L/sha] | Lerf,rigole [m] | Verf,rigole [m³] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 243.00 | 0.75 | 0.77 |
| 10 | 183.90 | 1.09 | 1.13 |
| 15 | 152.60 | 1.31 | 1.36 |
| 20 | 131.70 | 1.46 | 1.51 |
| 30 | 104.80 | 1.64 | 1.69 |
| 45 | 81.20 | 1.74 | 1.80 |
| 60 | 66.80 | 1.76 | 1.83 |
| 90 | 49.70 | 1.70 | 1.76 |
| 120 | 40.30 | 1.62 | 1.68 |
| 180 | 29.90 | 1.46 | 1.51 |
| 240 | 24.30 | 1.33 | 1.38 |
| 360 | 18.00 | 1.12 | 1.16 |
| 540 | 13.40 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| 720 | 10.90 | 0.78 | 0.81 |
| 1080 | 7.90 | 0.60 | 0.62 |
| 1440 | 6.50 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
| 2880 | 3.70 | 0.3 | 0.31 |
| 4320 | 2.90 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
c. Table for rough estimation of small systems with r15,n=0.2
| kf (m/s) | e.g. location Aachen (D) r15,0.2=152.6 L/sha | e.g. location Berlin (D) r15,0.2=213.1 L/sha | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A=100 m2 | A=150 m2 | A=200 m2 | A=100 m2 | A=150 m2 | A=200 m2 | ||
| 1*10-4 | Volume in m3 | 1.36 | 2.04 | 2.72 | 1.90 | 2.85 | 3.79 |
| 1*10-5 | Volume in m3 | 1.49 | 2.24 | 2.99 | 2.09 | 3.13 | 4.79 |
| 1*10-6 | Volume in m3 | 1.51 | 2.26 | 3.02 | 2.11 | 3.16 | 4.21 |
Rough estimation of retention volume
The following method of calculation can be used for a rough estimation of required retention volume with specified rain duration.
Example calculation:
- Permitted discharge from property: 1.5 L/sha
- Property size: 0.105 ha
- Rain yield r15(1) = 108 L/sha
- Rain yield r15(2) = 193 L/sha
| Surface | x | Runoff coefficient | x | Rain yield | = | Qr15(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 231 m2 | x | 1 | x | 0.0193 L/s x m2 | = | 4.46 L/s |
| 114 m2 | x | 0.8 | x | 0.0193 L/s x m2 | = | 1.76 L/s |
| Total rainwater runoff | Qrges | = | 6.22 L/s | |||
| Approved discharge quantity: | Qab | = | 0.105 ha (property size) x 1.5 L/sha | |||
| = | 0.158 L/s | |||||
| Rainwater quantity for retention: | Qs | = | Qr15(0.2)ges - Qab | |||
| = | 6.22 L/s – 0.158 L/s = 6.06 L/s | |||||
| Required backwater volume Verf: (The retention system must absorb Qs for 15 min.). | ||||||
| Verf | = Qs x 60 x 15 = Qs x 900 | |||||
| = 6.06 L/s x 900 s = 5.5 m3 | ||||||
Accurate dimensioning of a trench or retention system with planning software
Since calculation of the required trench volume is iterative, planning software such as the RAINPLANER is better designed for solving it.
Dimensioning surface infiltration
| As = Ared / (kr x sf x 107 / 2 x r D(n) –1) | |
|---|---|
| Ared | = connected paved surfaces |
| sf | = Joints proportion in a permeable paved area (0 < sf =< 1) |
| kr | = Permeability coefficient in the considered infiltration layer |
| rD(n) | = Rain yield |
| Example: | |
| Ared | = 300 m2 |
| sf | = 1 (INTEWA grass grid pavers) |
| kr | = 2 x 10-4 m/s |
| r D(n) | = from KOSTRA table with n=0.2/a and D=10 min: r10(0.2) = 204.60 L/sha |
| As = 300 / ( 2 x 10-4 x 1 x 107 / 2 x 204.6 –1) = 77 m2 | |
Dimensioning infiltration trenches behind small wastewater treatment systems
According to DIN 4261-1, version 2002, the water discharged from SWWTPs can be infiltrated through trenches in soils with kf = 5 x 10-7 to 5 x 10-3 m/s. As the base of infiltration system can clog up with time, only the side areas remain effective in the long run. A large retention volume is an advantage for variable infiltration efficiency i.e. during frost or uneven loading of the trench. The following simplified dimensioning methods shall apply according to DIN:
| Required wall area (m2/inhabitant value PE): | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 m2 / PE to 1.5 m2 / PE with: | Sand-gravel mixture, sand, light silty sand | |
| 2 m2 / PE to 2.5 m2 / PE with: | Silt (also light clay), sand-silt mixture, stone-loam mixture | |
| Required number for example of DRAINMAX Tunnel: | ||
| Base element | 2.25 m length x 0.8 m heigth x 2 sides | |
| As | = 3.6 m2 per tunnel without front walls | |
| PE | to 1.5 m²/PE | to 2.5 m²/PE |
| 4 | 1 pcs. | 2 pcs. |
| 8 | 1 pcs. | 4 pcs. |
| 12 | 3 pcs. | 6 pcs. |
| 16 | 4 pcs. | 8 pcs. |
A specified calculation must be done with other soil conditions and higher PE values.
Comparison between DRAINMAX Tunnel and pipe trench variants
According to EN 12566-3 for small wastewater treatment plants (SWWTPs) 150 L / day / inhabitant (PE) has the following daily distribution:
3h = 30%
3h = 15%
6h = 0%
2h = 40%
3h = 15%
7h = 0%
When using a classic pipe trench, the largest flow rate must be determined. This occurs within 2h with 40%. For a SWWTP with 5 PE this is calculated as follows:
40 % in 2 h from 750 L/day
=> 300 L/2h
=> 0.0417 L/s
When using the DRAINMAX Tunnel, the daily volume can be stored in the trench. The largest flow rate is then calculated as follows:
100 % in 24 h from 750 L/day
=> 750 L/24 h
=> 0.0087 L/s
=> this flow rate is 4.8 times smaller than with the pipe trench variant
=> the DRAINMAX tunnel can be dimensioned approx. 4.8 times smaller than the pipe trench
Legal framework conditions in Germany
When planning and installing an infiltration or retention system, the current versions of the following regulations must be observed:
| Scope | Policy | Content |
|---|---|---|
| Water supply | Arbeitsblatt DWA-A 138 | Planning, construction and operation of precipitation water infiltration systems |
| ATV-DVWK-M 153 | Recommendations for handling rainwater | |
| ATV-A 121 | local precipitation / heavy rainfall analysis according to return period and duration | |
| DWA-A 117 | Design of rain retention spaces | |
| Kostra | Heavy precipitation amounts for Germany | |
| DIN 4261-1, Kapitel 9 | Small wastewater treatment plants, transport underground of biologically treated wastewater | |
| EN 752 | Drainage outside of buildings… | |
| ATV A 118 | Hydraulic design and verification of drainage systems | |
| ATV A 118 | Guidelines for the design of rainwater discharge systems in mixed water sewers |
Obligations to notify and obtain license
| Scope | Policy | Content |
|---|---|---|
| EU legislation | Anzeige- und Genehmigungspflichten
EG-Directive 80/68/EWG / 1979 || Pollution resulting from the discharge of specific dangerous substances into community waters. Protection of groundwater against pollution by specific dangerous substances | |
| Federal legislation | Household water law WHG | In accordance with the WHG, infiltration plants require a licence, since 1996 the States have been able to abolish the licence requirement,
groundwater regulation |
| Building Code | Building Code | |
| State legislation | State Building Regulation | Specification of the type of system and size in the building application, most state building regulations meanwhile promote or demand the decentralized infiltration of precipitation water |
| Wastewater Regulation | Request for partial exemption from the obligation to connect and use the public sewage system. Obligation to declare prior to construction of the system at the municipal water utility | |
| State Water Law | possible obligation to infiltrate rainwater | |
| State Water Law | possible permission of the subsidiary water authority for infiltration | |
| kommunale Abwassersatzung | possible application for partial exemption from connection and compulsory use at the municipal water disposal company |